Next, let’s look at which industries and site types benefited and which ones took the biggest hit.
Which Websites Were Most Affected By Dec 2025 Google Core Update? (Winners vs Losers)
The December 2025 Core Update didn’t impact all websites equally. Visibility shifts followed clear patterns tied to intent clarity, experience depth, and topical authority, not niche size or brand fame alone.
Our experts analyzed 40 of our client sites to check how the Dec 2025 Core Update affected them. Below is a grounded breakdown of who gained and who lost, based on SERP movements we tracked across client portfolios and competitive landscapes.
Industries and Site Types That Gained Visibility
These were sites that already aligned closely with how users search, evaluate information, and make decisions, often without chasing SEO trends aggressively.
What worked well:
- Brand-led publishers with consistent topic ownership
- eCommerce sites offering first-hand product insights (use cases, comparisons, FAQs)
- Service businesses with experience-backed guides and outcome-focused pages
- Editorial content that answered primary and secondary queries in one place
Why they won:
- Clear match between query intent and page format
- Demonstrable experience (examples, screenshots, data, outcomes)
- Fewer but stronger pages with regular, meaningful updates
- Cohesive internal linking reinforces topical depth
In many cases, these sites didn’t publish more, but published better. Their stability came from clarity and consistency, not volume.
Industries and Site Types That Lost Visibility
Sites that declined often weren’t “bad,” but they failed to meet rising expectations around usefulness, credibility, and intent precision.
Commonly affected patterns:
- Thin affiliate and comparison sites are built on repetitive templates
- Scaled programmatic SEO is lacking differentiation
- AI-generated content without editorial oversight or real-world experience
- Mixed-intent pages attempting to rank for multiple, conflicting queries
Why they dropped:
- Low perceived usefulness despite keyword coverage
- Weak engagement signals (short dwell time, pogo-sticking)
- Shallow topical authority spread across too many URLs
- Content updates that changed wording, not value
In several cases, visibility declined gradually rather than overnight, indicating deprioritization, not punishment.
Dec 2025 Google Core Update – Winners vs Losers

This wasn’t an “industry-wide hit.” Within the same niches, we observed both winners and losers, depending entirely on execution quality and alignment with user expectations.
Before deciding on recovery actions, the next step is critical: confirming whether your site was truly impacted and where.
Let’s break down how to assess that accurately.
Also Read: Proven AEO Tactics to Drive Traffic From LLMs Like ChatGPT
How to Check If Your Site Was Impacted by Google’s Core Update?

Before making any recovery decisions, it’s critical to confirm whether your site was actually impacted by the December 2025 Core Update and, if so, how.
Core updates often coincide with seasonal shifts, tracking noise, or unrelated changes, which can lead to false conclusions.
Start with data, not assumptions.
Step 1: Confirm the Timing of the Drop
Use Google Search Console and compare performance across three windows:
- Pre-update baseline (4–6 weeks before rollout)
- Rollout period (during volatility)
- Post-update stabilization (2–3 weeks after completion)
If the decline began before or well after the rollout, the cause may not be the core update.
Step 2: Identify Site-Wide vs Page-Level Impact
Filter Search Console data by Pages and Queries to locate concentration areas. Not all drops signal a site-wide issue.
- Site-wide impact usually points to authority, trust, or systemic content problems.
- Page-level impact often indicates intent mismatch, outdated content, or competitive displacement.
Step 3: Focus on the Right Metrics
Avoid overreacting to isolated keyword drops. CTR fluctuations during core updates are common and often self-correcting.
Instead, track:
- Impressions (visibility signal)
- Clicks (actual traffic impact)
- Average position trends (directional insight)
- Query groups, not single keywords
Step 4: Rule Out False Positives
Before attributing losses to the update, check for:
- Indexing or crawl issues
- Manual site changes (content edits, internal linking, noindex tags)
- Tracking disruptions or analytics anomalies
Many “core update hits” turn out to be coincidental timing.
Step 5: Look for Stability Signals
Stability is as important as loss:
- Pages that hold rankings, which indicate what Google trusts
- These pages often contain recovery clues you can replicate elsewhere
A core update impact is rarely uniform. Precise diagnosis by page, query, and intent is the foundation of effective recovery.
Now that you know how to assess impact accurately, let’s look at what the December 2025 Core Update did to one of our clients and why our first response wasn’t to change anything.
What the December 2025 Core Update Did to Our Client Sites?
One of the biggest mistakes website owners often make after core updates is assuming that every ranking fluctuation requires immediate action. The December 2025 Core Update reinforced why restraint, when backed by experience and data, is often the smarter move.
Usually, between 15 Dec and 20 Jan, MSOfficeGeek.com observes a dip every year in traffic. This time, they were as it came during the Core Update rollout.
Apart from the seasonal dip, the client lost ranking of a few pages, and rankings dropped for 4 pages by the Google Core Update. But all in all, during and after the update, the site has remained stable.
Let’s have a detailed breakdown of this.
Impact Overview
The December 2025 rollout showed controlled movement rather than sharp declines.
- No sudden site-wide traffic drops
- Minor keyword reshuffling within existing ranking ranges
- Stable impressions across primary topic clusters
This stability wasn’t accidental. These sites had already been built on:
- Clear intent mapping
- Topical depth rather than content volume
- Consistent internal linking and authority reinforcement
Because there were no structural red flags, we deliberately avoided reactive changes during the rollout window.
Lessons From the 2021 and 2024 Core Updates
The calm response in 2025 was shaped by experience. In earlier updates, the client site saw:
- Traffic declines of up to 35%
- Ranking losses across high-intent pages
- Temporary visibility suppression despite stable backlinks
What mattered wasn’t the drop but how the recovery happened.
Root causes identified:
- Intent dilution across similar pages
- Over-expansion into loosely related topics
- Content updates focused on keywords, not usefulness
What actually drove recovery:
- Consolidating overlapping content
- Strengthening topic ownership instead of publishing more
- Improving internal linking to reinforce authority
- Updating content with real-world examples and clarity
Recovery didn’t come from overhauls. It came from minor, deliberate adjustments applied over time.
These lessons were already embedded into the content system; the December 2025 update didn’t require “fixes.” The groundwork had been done years earlier.
Next, let’s unpack why some sites recover without making any changes at all and when waiting is the right strategy.
Why Some Sites Recover Without Making Any Changes
One of the most misunderstood aspects of core updates is recovery timing. Not every site that dips needs immediate intervention, and in many cases, doing nothing is a strategic decision, not neglect.
The December 2025 Core Update followed Google’s long-standing approach: it re-evaluates content relative to competing results, rather than applying penalties or permanently downgrading sites.
In simple terms, this means that rankings can fluctuate during rollout, and pages may also temporarily lose visibility as systems recalibrate.
In such cases, recovery often occurs without any on-page changes when the reassessment stabilizes. We say this based on our past 201 and 2024 major updates.
Let’s discuss a few things that every website owner and SEO enthusiast must keep in mind.
Trust and Consistency Matter More Than Speed
With years of handling sites in multiple niches and overseeing multiple Google Core updates, our experts observed that sites that recovered on their own typically shared these traits:
- Long-term topical consistency
- Stable historical performance across updates
- Clear authorship and content ownership
- Minimal reliance on trend-driven content
Google appears to factor historical reliability when reassessing relevance, which explains why established content systems often regain visibility naturally.
Why Recovery Often Lags the Rollout
Recovery rarely aligns perfectly with rollout completion. This lag leads many site owners to make premature changes that can delay or suppress recovery.
Common reasons include:
- Deferred reprocessing of large content sets
- Gradual engagement data normalization
- Competitive reshuffling rather than direct demotion
Waiting is justified when drops are limited to position ranges (e.g., drop of rankings from 3 to 6 or 5 to 9). In most cases, impressions remain stable or even increase.
Your Core topic pages hold rankings, and no new technical or indexing issues are identified. In such cases, observation provides clearer signals than intervention.
Therefore, recovery isn’t always earned through fixes. Sometimes, it’s earned through consistency and patience.
Next, let’s understand the exact content strategy framework we use at ZeroToNineMarketing for our clients to help them stabilize and recover across core updates.
Our Proven Content Strategy To Recover From Google Core Update

Recovering from a core update isn’t about chasing signals; it’s about building a content system that consistently aligns with user intent, authority, and trust.
This is the framework we follow at ZeroToNineMarketing to help clients rank in search engines and GenAI Engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini.
Over the past 10 years, it has helped us stabilize visibility across updates, including December 2025.
Let’s understand the exact framework in brief.
Search Intent & SERP Reality Research
Every recovery starts with understanding what Google is actually ranking, not what we want it to rank.
We analyze:
- Dominant SERP formats (guides, lists, comparisons, FAQs)
- Presence of AI Overviews, PAA, and rich results
- Query modifiers indicating intent shifts (informational vs commercial)
If the SERP expects depth, surface-level updates won’t work. If it expects clarity, long-form content may underperform.
Competitor & Authority Gap Analysis
Ranking competitors often win on credibility, not SEO tactics. The goal isn’t imitation, it’s identifying authority gaps we can fill meaningfully.
We evaluate:
- Depth of coverage
- Experience indicators (examples, data, outcomes)
- Content freshness and maintenance
- Internal linking strength
Using E-E-A-T in Content Writing
E-E-A-T isn’t a checklist; it’s how content feels to a user. Experience signals are embedded naturally, not artificially added.
We reinforce it through:
- First-hand insights and practical explanations
- Clear authorship and accountability
- Updated references and contextual linking
- Avoiding generic, AI-style phrasing
Content Structure That Survives Updates
Structure affects both users and algorithms. This improves engagement and makes content easier for search systems to interpret.
We optimize for:
- Clear H1–H3 hierarchy
- Answer-first sections
- Short paragraphs and scannable layouts
- Logical progression of ideas
FAQ Schema & Entity Optimization
Schema is applied only when FAQs add real value and not to inflate markup.
FAQs are used selectively to:
- Address follow-up queries
- Support AI summaries
- Improve topical completeness
Internal Linking Strategy
Internal links distribute trust. Putting your ranking articles
We focus on:
- Strengthening priority pages by linking ranking articles in new pages.
- Removing orphan content that creates a negative impact on your search.
- Using contextual anchors that reflect intent.
- Reinforcing topical clusters by linking relevant topics in the content.
External Linking & Trust Signals
Outbound links help establish credibility. This signals transparency and confidence, not leakage.
We link to:
- Authoritative sources
- Relevant industry references
- Supporting documentation where needed
Recovery isn’t driven by isolated optimizations. It’s the outcome of a cohesive content strategy designed to withstand algorithm recalibration.
Next, let’s examine how UX, engagement, and performance signals influenced outcomes after the December 2025 Core Update.
UX, Engagement & Core Web Vitals After the Update
While content quality drove most ranking shifts in the December 2025 Core Update, user experience and engagement signals played a supporting and meaningful role.
These signals didn’t override relevance, but they often acted as tie-breakers between similarly strong pages.
UX Is About Clarity, Not Just Speed
Google’s expectations around UX have matured. It’s no longer about perfect scores but about frictionless consumption.
What mattered most:
- Clear page layout and visual hierarchy
- Readable typography and spacing
- Minimal intrusive elements (pop-ups, aggressive CTAs)
- Fast access to the primary answer
Pages that buried answers under intros or clutter struggled to hold attention.
Engagement Signals That Correlated With Stability
Across impacted and stable pages, we consistently observed differences in:
- Dwell time – users staying long enough to consume content
- Scroll depth – indicating real engagement, not skimming
- Pogo-sticking – users bouncing back to search results
Pages that satisfied intent early and expanded logically performed better during reassessment.
Core Web Vitals: Baseline, Not a Silver Bullet
Core Web Vitals acted as a hygiene factor, not a recovery lever. Sites with poor CWV rarely gained, but improving scores alone did not reverse core update losses.\
What is the role of each Core Web Vital in Recovery:
- LCP: Must be acceptable, not perfect
- INP: Impacts interaction-heavy pages
- CLS: Affects perceived trust and usability
UX Mistakes That Hurt Post-Update Performance
These issues weakened engagement, indirectly affecting rankings:
- Overloading pages with ads or widgets
- Auto-playing media without context
- Forcing users through unnecessary navigation
- Prioritizing design over readability
UX and performance don’t replace content quality, but they amplify it. When content relevance is similar, the page that’s easier to read, navigate, and trust tends to win.
Next, let’s address a critical expectation-setting question: how long recovery actually takes after a Google Core Update.
How Long Does Recovery Take After a Core Update?
One of the most common and most frustrating questions every website owner has after a core update: “How long does recovery actually take?”
The shortest and honest answer is “recovery timelines vary, but they are rarely immediate.”
Typical Recovery Timelines
Based on patterns observed across multiple core updates:
- Short-term fluctuations (days–2 weeks):
Normal reshuffling during rollout. Rankings may move up and down without indicating long-term impact. - Early stabilization (2–6 weeks):
Visibility begins to settle. Sites aligned with intent and quality often regain lost positions without changes. - Meaningful recovery (1–3 months):
For sites that require improvements, recovery usually starts after Google reprocesses updated content. - Full reassessment (3–6 months or next core update):
Larger structural or authority issues may only be resolved over longer cycles.
Core updates don’t re-rank pages in isolation. Google reassesses content usefulness across the entire topic, engagement, and satisfaction signals over time and relative quality against competitors. This makes quick reversals unlikely even after strong fixes.
When to Act vs When to Wait
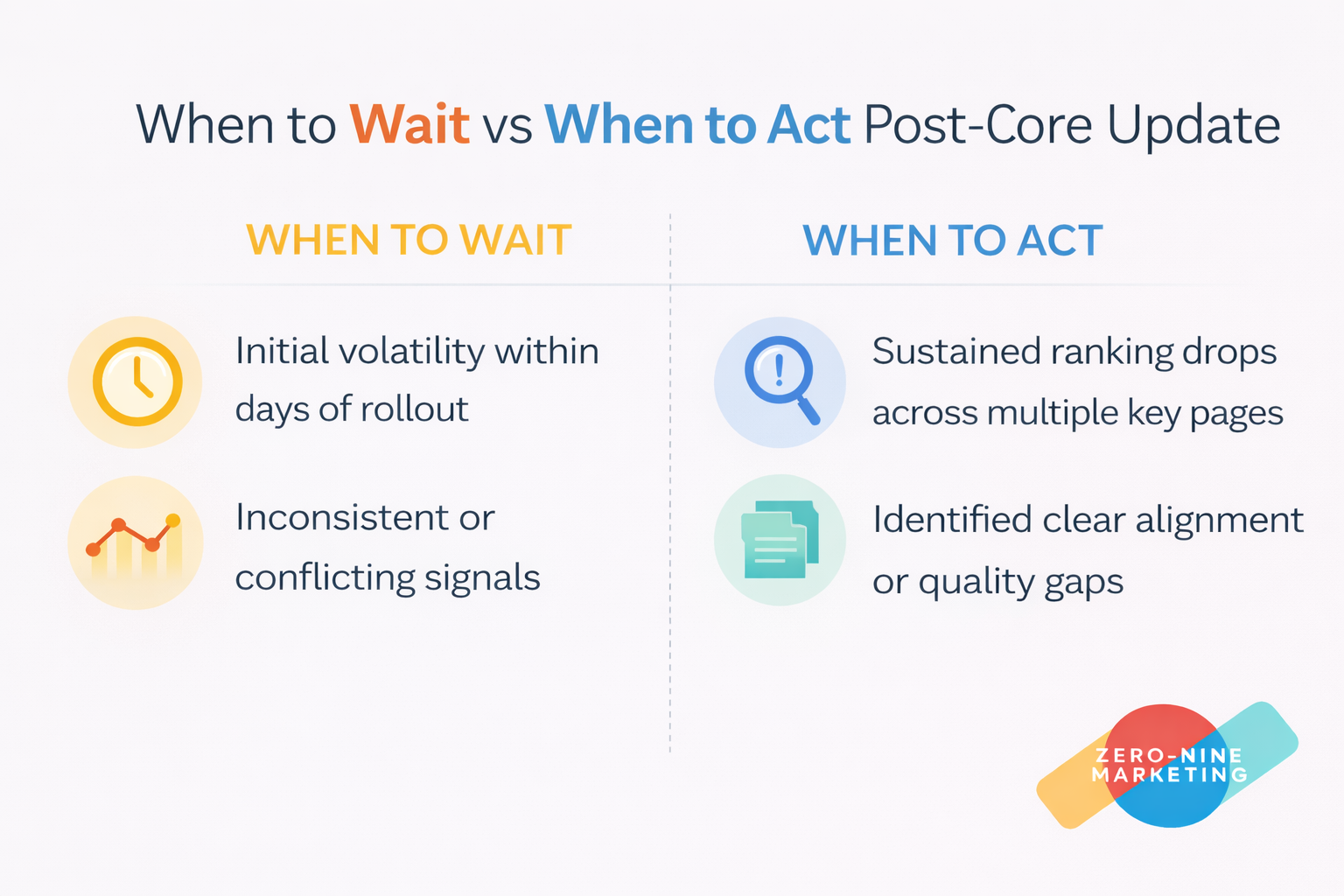
Avoid tracking single keywords. Instead, monitor query group visibility, page-level impression trends, and engagement improvements over time. Remember one thing: recovery is often gradual, not dramatic.
Core update recovery is a process, not an event. Sites that recover fastest are those that diagnose accurately, improve deliberately, and allow time for reassessment.
Next, let’s look at common recovery mistakes that can slow or completely block progress.
Common Recovery Mistakes to Avoid
After a core update, the biggest damage often comes not from the update itself, but from how sites react to it. Over the years, we’ve seen the same recovery mistakes repeated, many of which slow down or completely block progress.
Avoid these pitfalls.
Making Panic Changes During the Rollout
Core updates roll out over days or weeks, and volatility during this period is expected. Making content edits, restructuring pages, or changing internal links while rankings are still fluctuating introduces unnecessary variables.
These changes make it difficult to understand whether losses were caused by the update or by your own actions. In many cases, sites that would have stabilized naturally end up prolonging recovery due to premature interventions.
Deleting or Noindexing Content Too Quickly
A drop in rankings does not automatically mean content is low quality or irrelevant. Pages are often reassessed temporarily during core updates and may recover once systems stabilize.
Deleting or noindexing such pages without diagnosing intent mismatch, freshness issues, or competitive gaps removes the possibility of recovery through refinement. In practice, many of these pages need clarity and not removal.
Over-Optimizing for a Single Update
Trying to “optimize for the update” is a recurring mistake. This usually results in forced keyword usage, artificial E-E-A-T signals, or unnatural internal linking patterns.
While these changes may look strategic in the short term, they often weaken trust and readability. Core updates reward sustained usefulness and consistency, not reactive optimization tactics.
Blindly Copying Top-Ranking Competitors
Competitor analysis is valuable, but copying competitors without understanding why they rank rarely works.
Many top-ranking pages benefit from long-standing authority, brand trust, and historical engagement signals that can’t be replicated through structure or word count alone.
Replicating surface-level elements often leads to generic content that fails to differentiate or add value.
Ignoring Pages That Stayed Stable
Focusing only on pages that dropped is another overlooked mistake. Pages that remained stable during the update often hold the clearest signals of what Google trusts.
They have strong intent alignment, clear structure, and effective internal support. These pages should inform recovery decisions more than the ones that fluctuated the most.
Recovery efforts fail when actions are rushed or reactionary. Sustainable recovery comes from understanding what worked, fixing what truly underperformed, and aligning content with real user expectations—not from chasing the update itself.
Next, let’s conclude the discussion about the December 2025 Google Core Update and what it means going forward.
Conclusion
The December 2025 Google Core Update made one thing clear: sustainable rankings come from user-focused content, not reactive SEO tactics. Sites that aligned with intent, authority, and usefulness remained stable or recovered over time.
Core updates will continue to evolve, but the principle stays the same. When content is built to genuinely help, user updates become far less disruptive. Recovery isn’t about chasing algorithms. It’s about building trust at scale.
If your site was impacted by the 2025 Google Core Update and you want a clear, data-backed recovery plan (not generic advice), let’s talk.
Book a strategy call or contact us through email to get clarity on what to fix, what to ignore, and how to move forward with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can backlink quality alone help recover from the 2025 Google Core Update?
Backlinks can support recovery, but they rarely fix core update losses on their own. If content intent, depth, or authority signals are weak, even strong backlinks won’t restore rankings sustainably.
Should I pause content publishing after a core update?
Pausing isn’t necessary, but publishing without clarity is risky. New content should be aligned with validated user intent and topical authority, otherwise, it may dilute recovery efforts.
Does updating content frequency affect recovery speed?
Frequency matters less than quality and relevance. Strategic updates to key pages tend to outperform frequent but superficial edits across many URLs.
Can AI-generated content recover after the 2025 Google Core Update?
Yes, but only when it’s heavily edited, experience-led, and genuinely useful. AI-generated content without human insight or differentiation struggled the most during this update.
How ZeroToNine Marketing's approach helps core update recovery differently?
We focus on diagnosis before action. Instead of applying generic fixes, we identify intent gaps, authority weaknesses, and structural issues using real update data. After this build recovery strategies designed to hold through future core updates, not just the current one.
